How to Create a Relative Frequency Table in Excel – 5 Steps
Relative frequency is the ratio of a frequency within a specific range to the total number of frequencies. The percentage or dominance of a class range over the overall range can be determined using relative frequency.  The sample dataset showcases people’s weight. To determine the frequency of each class:
The sample dataset showcases people’s weight. To determine the frequency of each class: 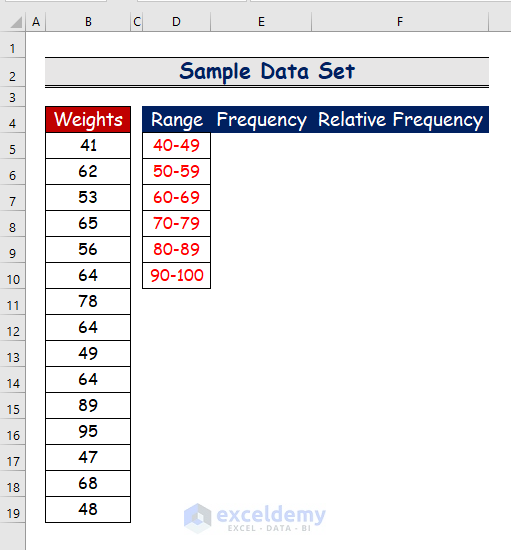
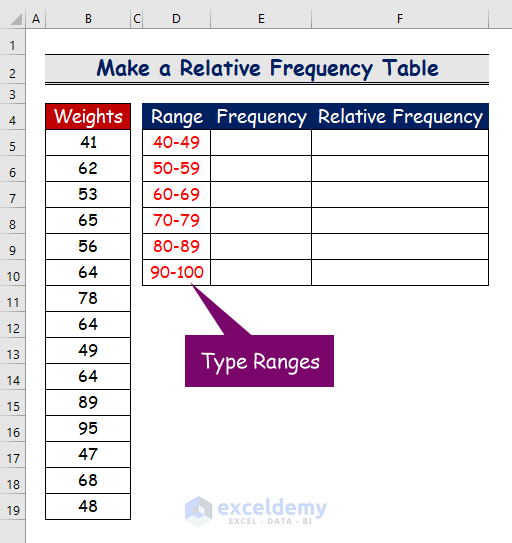
Step 1- Specify the Range of Weights
- Specify the range with an equal interval. Here, a range from 40to 100with an equal interval of 10.
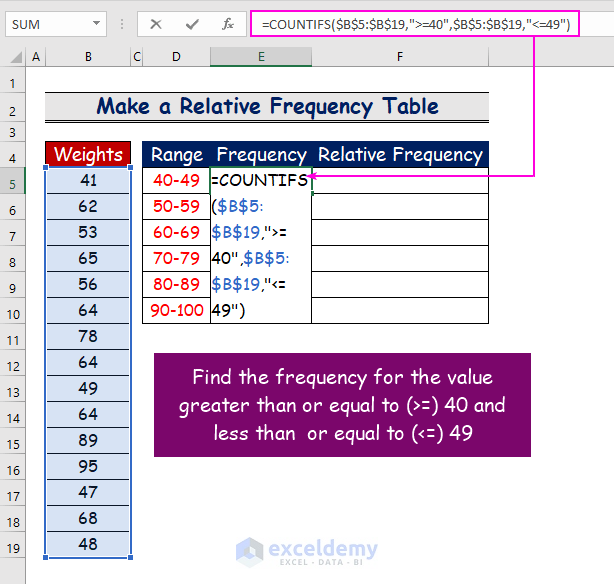
Step 2 – Use the COUNTIFS Function to Count the Frequency
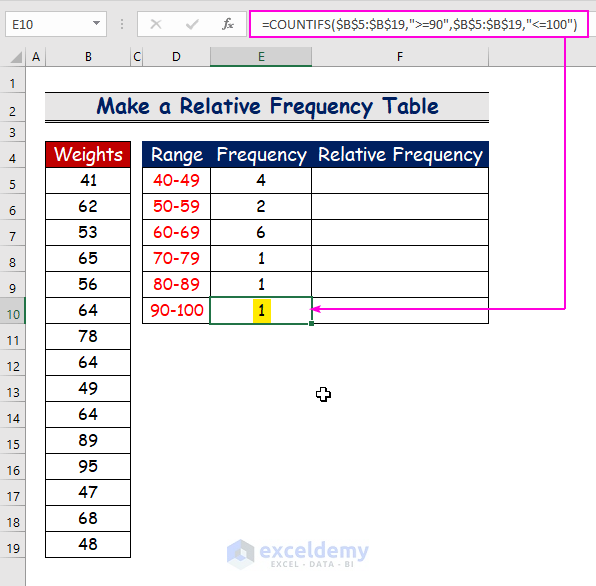
To count the frequency for the range 40–49:
- In E5, use the conditions greater than or equal to 40and less than or equal to 49as the criteria argument:
=COUNTIFS($B$5:$B$19,">=40",$B$5:$B$19," <=49")
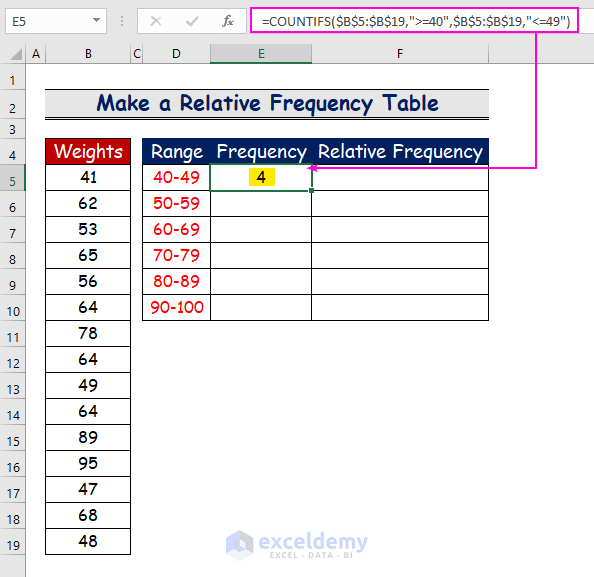
- Use the same function for the other ranges. For example, in E10, use the following formula:
=COUNTIFS($B$5:$B$19,">=90",$B$5:$B$19," <=100")
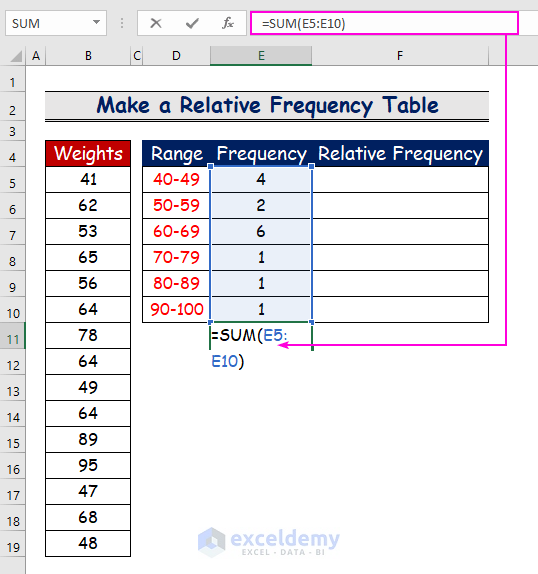
Step 3 – Use the SUM Function to Count the Total Frequency
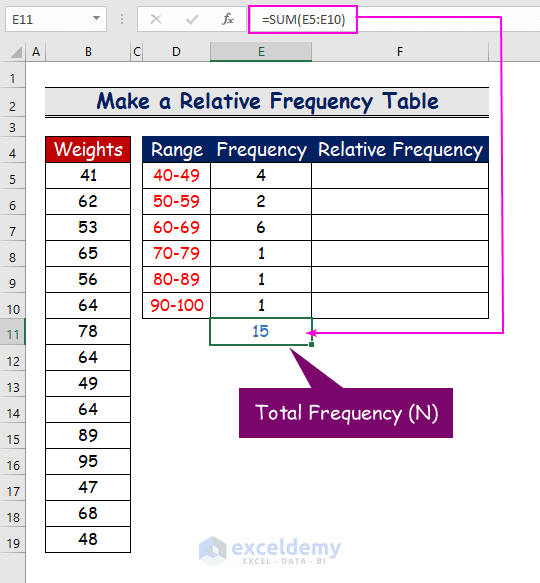
- To count the total frequency of the dataset, enter the following formula:
=SUM(E5:E10)
Step 4 – Use a Formula to Create a Relative Frequency Table
- Divide the frequency of each cell by the total frequency to find the relative frequency.
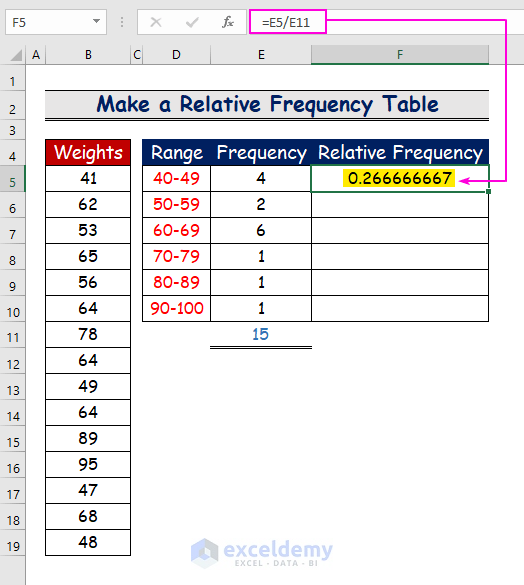
- For the cell value in E5(4), use the following formula.
=E5/E11
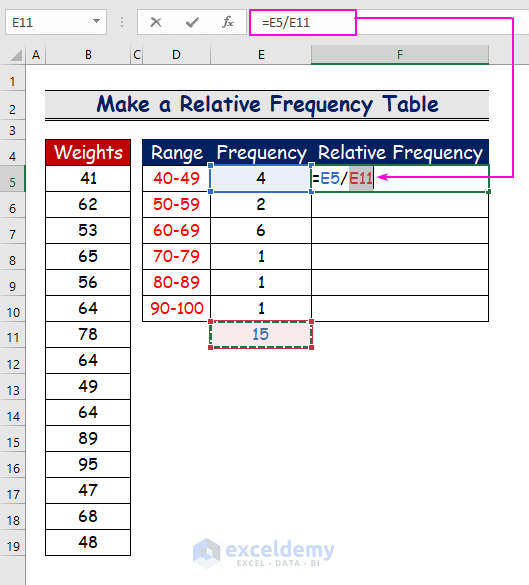
The output is 0.2666667: the relative frequency of the range 40–49.
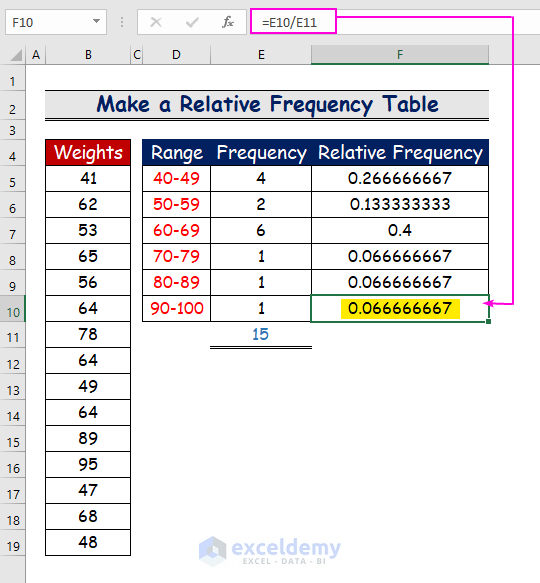
- Repeat the procedure for the other ranges.
- The relative frequencytable will be displayed.
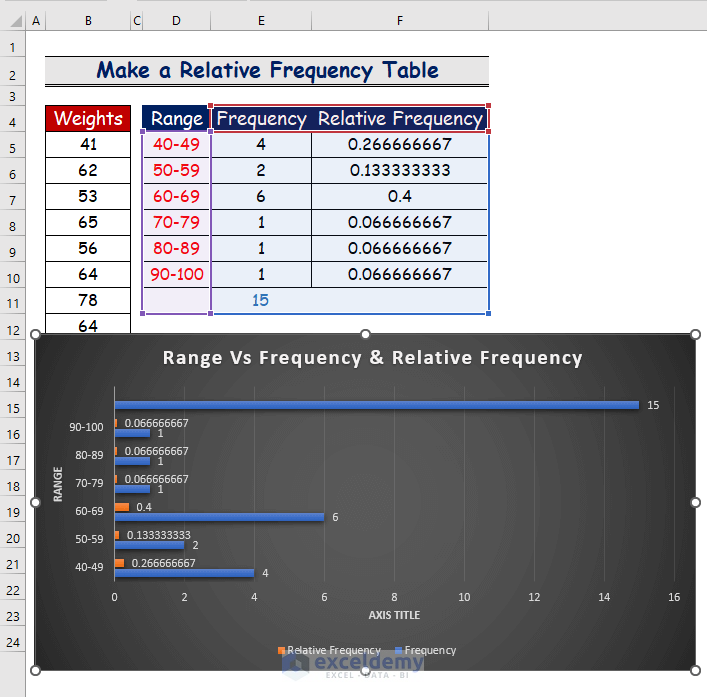
Step 5 – Insert a Chart with a Relative Frequency Table
- In the Inserttab, select a chart.
- The orangecolor denotes therelative frequency of a given range, whereas the bluecolor denotes the frequency of that specific range.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- How to Make an Ogive Graph in Excel
- How to Do Cross Tabulation in Excel

 The sample dataset showcases people’s weight. To determine the frequency of each class:
The sample dataset showcases people’s weight. To determine the frequency of each class: 
 The sample dataset showcases people’s weight. To determine the frequency of each class:
The sample dataset showcases people’s weight. To determine the frequency of each class: 









